Little Snitch 4.5
I had the latest stable version of Little Snitch on my Mac with macOS High Sierra. After I installed macOS Mojave beta, LS broke. But I also experienced: - Almost unresponsive system, probably caused by Little Snitch using 99% CPU. Killing LS wasn't possible because of agents restarting LS. Without a license key, Little Snitch runs in demo mode, which provides the same protection and functionality as the full version. The demo runs for three hours, and it can be restarted as often as you like. The Network Monitor expires after 30 days. Turn it into a full version by entering a license key.

A powerful and versatile application that enables you to monitor the network traffic and intercept unwanted connection attempts.
- Little snitch mojave cracked. Little Snitch is usually a well-known Mac PC application. It detects outbound contacts and collects guidelines to stop those connections. As soon as set up, Small Snitch screens your web visitors. Every period it detects an outbound link. Open the “LittleSnitch-4.0.5.dmg” file.
- If you’re using the free version of Little Snitch, you have to deal with the fact that it automatically quits after every three hours. To avoid this, you have to buy the full version. If you’ve been looking for a free Little Snitch alternative that works with macOS Mojave and previous macOS versions, Lulu is what you need.
Objective Development then issued Little Snitch 4.2.1 to fix a bug that caused an alert to be shown for an invalid code signature for the App Store in Mojave for some users. This latest update also resolves a bug with duplicating rules, improves Dark mode support, and brings back the capability to use the dark appearance of Little Snitch.
Track background activityAs soon as your computer connects to the Internet, applications often have permission to send any information wherever they need to. Little Snitch takes note of this activity and allows you to decide for yourself what happens with this data.
Control your network
Choose to allow or deny connections, or define a rule how to handle similar, future connection attempts. Little Snitch runs inconspicuously in the background and it can even detect network-related activity of viruses, trojans, and other malware.
Filter connections and monitor your network traffic with ease
The Little Snitch Network Monitor utility features a well-designed interface and provide easy-to-read animated and informative diagrams created based on real time traffic information. Hence, you can analyze bandwidth, connectivity status, traffic totals, detailed traffic history for the past hour and more.
You can filter the displayed data based on the process name or server port and group them according to your needs. Little Snitch helps you view traffic peaks, check the average bandwidth and save snapshots for further analysis.
Enable the Silent Mode for a distraction free working environment
The network traffic can be easily captured in the PCAP format while the network activity is displayed along various system events in order to provide a context. There is also a Silent Mode that allows you to get on with your work without being interrupted by any network related notifications. However, you can review the Silent Mode Log to create rules for connection attempts that took place during this period.
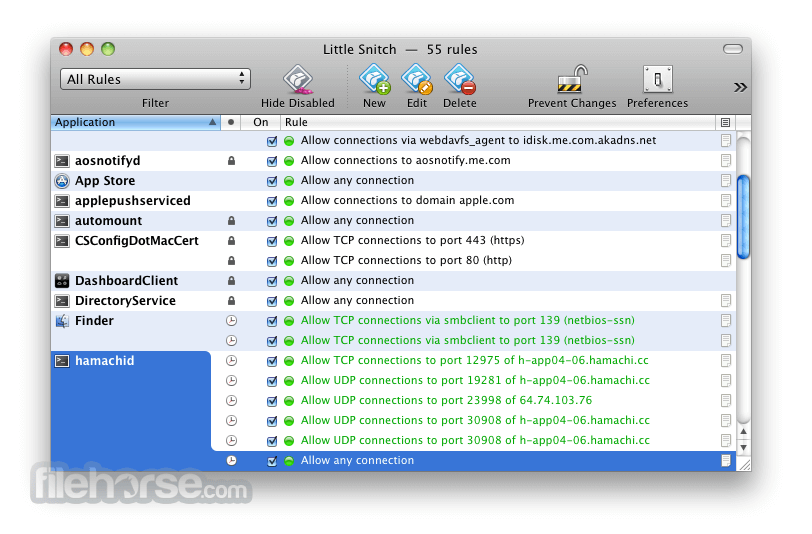
On top of that, you can group your rules in different profiles and enable them only when a particular profile is active. Thanks to Little Snitch’s status bar menu, you can choose the desired profile with just a few mouse clicks.
Download Little Snitch For Windows
Enjoy the versatility of the Automatic Profile Switching function
At the same time, you can take advantage of the Automatic Profile Switching feature and associate different networks with certain profiles. Once the network is detected, the associate profile is automatically enabled. For example, you can use a set of filters when you are at home and more restrictive ruleset when you access the web from an Internet Cafe.
What is more, Little Snitch features a flexible temporary rule system that offers a number of options for rules that are effective only for a limited period of time. Furthermore, Little Snitch automatically analyzes your ruleset and indicates the presence of overlapping, redundant or invalid rules that you might want to delete.
What's New:
Version 4.5 (5462):This release brings new features and improvements requested by users, after a few months of focussing on compatibility with macOS Catalina. In particular:
Redesigned Research Assistant in Connection Alert
Little Snitch Mac Os Mojave Crack
Since our Internet Access Policy initiative (IAP) gains popularity and support by more and more third party developers, the IAP has been made the main focus of the Research Assistant. It provides you with first hand information directly from the app developer.
The information from our Research Assistant online database now comes bundled with Little Snitch to supplement processes which don’t have an IAP of their own. It’s therefore no longer necessary for Little Snitch to connect to the online database to retrieve this information.
Along with connection details and possible warnings regarding code identity checks all this information is now presented in a redesigned interface, in a clear and consistent manner.
Little Snitch Download
Other improvements in the Connection Alert- The connection alert now offers a wider range of options for the lifetime of temporary rules, ranging from 1 minute up to 30 days.
- When a code identity check fails, it’s now always possible to “accept the modification” and update the identity check, using the executable’s cryptographic hash if nothing else is suitable.
- When no server name can be derived and only the IP Address of a remote computer is shown, it’s now possible to create rules for the entire subnet, not just the particular IP Address.
Improvements in Network Monitor

- Network Monitor now shows accesses to the Berkeley Packet Filter (BPF), and rules for this kind of access can now be managed from within Network Monitor as well.
- Since BPF access can now be managed in Network Monitor, BPF related connection alerts no longer appear in Silent Mode.
- All server names ending in .local are now grouped in one single “local” domain.
- Improved rule creation from within Network Monitor. If a similar but currently disabled rule already exists, it is replaced by the newly created rule.
- The context menu for a connection now offers an “Until Logout” option when the Shift key is held.
- Fixed an issue where Network Monitor stopped showing connections.
- Fixed an issue where macOS would change Spaces when a full screen app is active and Network Monitor is brought to front.
- Fixed: When there are no rules matching a connection, buttons for rule creation are only shown when the mouse is at the prospective button location. This prospective location was sometimes off by half a button width, making it hard to create an allow-rule. This issue has been fixed.
- Fixed an issue where geographic labels on the map could be off by half a map width.

Improvements in Little Snitch Configuration
Little Snitch Mac
Little Snitch Osx Mojave 1
- Improved editing of a selection of multiple rules.
- In order to derive code identity information, Little Snitch Configuration must read the executable files of processes. If an executable cannot be read due to file permissions, we now derive code identity information via a privileged component.
- Improved the selection of suitable sections from the Internet Access Policy of a process.
- Little Snitch now ships with built-in Internet Access Policy information for further macOS system components.
- Improved selection of relevant information from Internet Access Policy in Network Monitor.
- Updated Welcome Window in Little Snitch Configuration to reflect the new design of the connection alert.
- After a fresh installation Little Snitch Configuration no longer shows factory rules in the “Last 24 Hours” section.
- Preventing the simultaneous display of modal alert windows, possibly covering each other. They are now displayed one after the other.
- Fixed detection of remote endpoint name for Viscosity VPN.
- Fixed a crash of Little Snitch when other programs write garbage to the System Configuration. This crash occurred with a Microsoft Active Directory client for macOS.
- Numerous other bug fixes and improvements.
Screenshots:
- Title: Little Snitch 4.5
- Developer: Objective Development Software GmbH
- Compatibility: macOS 10.10 or later, 64-bit processor
- Language: English
- Includes: Serial
- Size: 40.33 MB
- visit official website
Little Snitch Osx Mojave Full
This release contains changes in the following areas:
Improved detection of program modification
Little Snitch has a security mechanism that ensures rules are only applied to programs for which they were originally created. This is to prevent malware from hijacking existing rules for legitimate programs. To do that, Little Snitch must be able to detect whether a program was modified. How Little Snitch does that changes with this version.
Previous versions required a program to have a valid code signature in order to be able to detect illegitimate modifications later on. Programs without a code signature could not be validated and Little Snitch warned accordingly. The focus was therefore on a program’s code signature.
Beginning with version 4.3, Little Snitch can always check whether a program has been tampered with, even if it’s not code signed at all. The focus is now on checking for modifications with the best means available. That is usually still the code signature but for programs that are not code signed, Little Snitch now computes a secure hash over the program’s executable. (There’s still a warning if a process is not signed, but only to inform you about a possible anomaly.)
This change leads to a different terminology. When editing a rule, Little Snitch Configuration no longer shows a checkbox titled “requires valid code signature” but instead one that is titled “check process identity” (or if the rule is for any process: “apply to trusted processes only”).
Instead of a “code signature mismatch”, Little Snitch’s connection alert now informs that “the program has been modified”.
In cases where Little Snitch detects such a modification, it now also better explains the possible underlying cause and the potential consequences.
For more information see the chapter Code identity checks in the online help.
Configuration File Compatibility
This version uses a new format with speed and size improvements for the configuration file in which the current rule set and the preferences are stored. This new file format is not compatible with older versions of Little Snitch, though.When updating to Little Snitch 4.3, the old configuration file is left untouched in case you want to downgrade to a previous version of Little Snitch. All changes made in Little Snitch 4.3 or later are not included in the old file, of course.Note that backup files created using File > Create Backup… in Little Snitch Configuration use the old file format and are therefore backward-compatible with previous versions of Little Snitch.
Improved Support for macOS Mojave
- Improved appearance in Dark Mode.
- Fixed backup restore from Time Machine not working in Little Snitch Configuration due to the new “Full Disk Access” security mechanism.
- Fixed creating Diagnostics Reports for non-admin users (on macOS High Sierra and later). When you contact our tech support, we sometimes ask you to create these reports.
Little Snitch Osx Mojave 2
Performance Improvements
- Improved overall performance for large rule sets.
- Reduced CPU load of Little Snitch Daemon during DNS lookups.
- Reduced CPU load of Network Monitor while inactive.
- Improved performance of rule sorting in Little Snitch Configuration, which leads to better overall performance.
- Fixed Little Snitch Daemon hanging while updating a rule group subscription that contains many rules.
- Fixed a memory leak that occurred when closing a snapshot window in Network Monitor.
Little Snitch Osx Mojave Download
Internet Access Policy
- Fixed an issue causing an app’s Internet Access Policy not being shown if that app was running in App Translocation.
- Fixed clickable links not working in the “Deny Consequences” popover when creating rules in connection alert or Network Monitor.
- Internet Access Policy file: Fixed large values for a connection’s “Port” being rejected.
Process Identity and Code Signature Check Improvements
- Added support for detecting revoked code signing certificates when checking a process’ code signature. The connection alert and Network Monitor now treat such processes like processes without a valid code signature and show relevant information. Also, rules created will use an appropriate identity check (based on the executable’s checksum, not based on the code signature).
- When showing a connection alert for a process that has no valid code signature, Little Snitch now tries to find out if loading a shared library may have caused the issue with the code signature. If so, this is pointed out in the connection alert.
- Fixed handling of app updates while the app is still running: Previous versions of Little Snitch would complain that the code signature could not be checked if the running app was replaced on disk, e.g. during an update.
- Fixed an issue where connection alerts would erroneously contain a warning that an application’s code signing certificate was unacceptable. This mainly happened when a process’ first connection was an incoming connection.
Improved Handling of Connection Denials and Override Rules
Little Snitch Osx Mojave Review
- Improved handling of override deny-rules that were created as a consequence of a suspicious program modification (“Connection Denials”). In Network Monitor, these rules are now marked with a dedicated symbol. Clicking that symbol allows to remove that override rule, if the modification is confirmed to be legitimate.
- Changed override deny-rules created for failed code identity checks to not be editable or deletable. Instead, double-clicking such a rule allows you to fix the underlying issue, which then automatically deletes the override rule.
Little Snitch Mac Mojave
UI and UX Improvements
- Automatically combine rules: For improved handling of large rule sets with many similar rules that only differ in host or domain names. This is common when subscribing to blocklists, which may contain thousands of similar, individual rules denying connections to various servers. The new “Automatically combine rules” option in Little Snitch Configuration (on by default) now combines such similar rules into a single row, making it much easier to keep track of large lists of rules.
- Improved appearance when Accessibility option 'Increase contrast' is active.
- Improved floating window mode in Network Monitor.
- When choosing File > Restore from Backup in Little Snitch Configuration, the list showing possible backup files now includes backups that Little Snitch created automatically.
- Improved the map shown in the “Known Networks” window in Little Snitch Configuration.
- Improved the legibility of traffic rates in the status menu on Retina displays.
- Fixed data rates shown in Network Monitor to match the values shown in the status menu.
- Fixed the “Duration” setting in Preferences > Alert > Preselected Options not being respected.
- Fixed an issue with “undo” when unsubscribing from a rule group or when deleting a profile.
- Fixed an issue in Little Snitch Configuration where the “Turn into global rule” action did not work.
- Fixed an issue where an error that occurred in the course of a previous rule group subscription update was still displayed, even though the problem no longer existed.
Other Improvements and Bug Fixes
Little Snitch Mojave
- Increased the maximum number of host names allowed in a rule group subscription to 200.000.
- Fixed an issue causing XPC services inside bundled frameworks to not be recognized as XPC. This resulted in connection alerts to be shown for the XPC services themselves instead of for the app the service belongs to.
- Fixed an issue causing Time Machine backups to Samba servers to stop working under some circumstances.
- Fixed an issue related to VPN connections with Split DNS configuration that caused only the server’s IP address to be displayed instead of its hostname.
- Reduced the snap length in PCAP files, allowing them to be analyzed not only with Wireshark but also with “tcpdump”.