- Arduino Tutorial
- Arduino Function Libraries
- Arduino Advanced
- Arduino Projects
- Arduino Sensors
- Motor Control
- Arduino And Sound
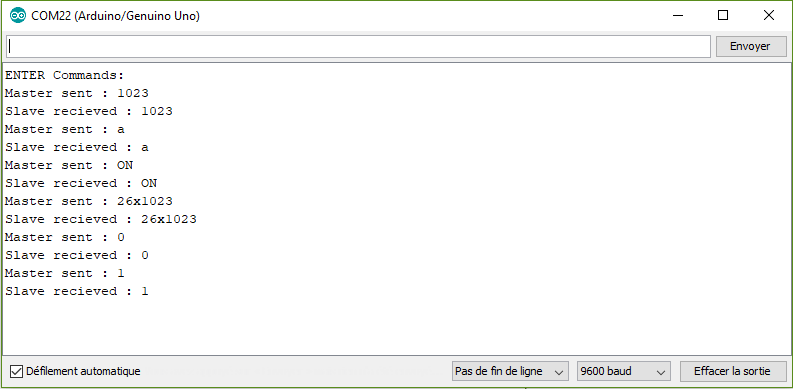
Im using an encoder motor, i want to move for N steps the motor forward (positive number) or backward (negative number), i insert the number of step in serial input. I can read only positive number. Thanks for help. How suggest Majenko i made a partial solution. Read just reads one character from the serial buffer and returns it (promoted to an int) or -1 if there's nothing to read. Read will not convert anything from ascii so if you send a '1' from the serial monitor it will read 49 (the ascii code for '1'). In your code you are comparing what you read to an ascii value since you compare to '1'. MyByte = Serial.read; // read in the next byte It is important to know that characters typed into the serial terminal (or sent from on Arduino to another via serial) are interpreted as ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) characters and encoded with the decimal number corresponding to the character on the ASCII table. MyByte = Serial.read; // read in the next byte It is important to know that characters typed into the serial terminal (or sent from on Arduino to another via serial) are interpreted as ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) characters and encoded with the decimal number corresponding to the character on the ASCII table. Serial.available returns the number of characters (i.e. Bytes of data) which have arrived in the serial buffer and that are ready to be read. Serial.read returns the first (oldest) character in the buffer and removes that byte of data from the buffer.
- Arduino Useful Resources
- Selected Reading
An array is a consecutive group of memory locations that are of the same type. To refer to a particular location or element in the array, we specify the name of the array and the position number of the particular element in the array.
The illustration given below shows an integer array called C that contains 11 elements. You refer to any one of these elements by giving the array name followed by the particular element’s position number in square brackets ([]). The position number is more formally called a subscript or index (this number specifies the number of elements from the beginning of the array). The first element has subscript 0 (zero) and is sometimes called the zeros element.
Thus, the elements of array C are C[0] (pronounced “C sub zero”), C[1], C[2] and so on. The highest subscript in array C is 10, which is 1 less than the number of elements in the array (11). Array names follow the same conventions as other variable names.
A subscript must be an integer or integer expression (using any integral type). If a program uses an expression as a subscript, then the program evaluates the expression to determine the subscript. For example, if we assume that variable a is equal to 5 and that variable b is equal to 6, then the statement adds 2 to array element C[11].
A subscripted array name is an lvalue, it can be used on the left side of an assignment, just as non-array variable names can.
Let us examine array C in the given figure, more closely. The name of the entire array is C. Its 11 elements are referred to as C[0] to C[10]. The value of C[0] is -45, the value of C[1] is 6, the value of C[2] is 0, the value of C[7] is 62, and the value of C[10] is 78.
To print the sum of the values contained in the first three elements of array C, we would write −
To divide the value of C[6] by 2 and assign the result to the variable x, we would write −
Declaring Arrays
Arrays occupy space in memory. To specify the type of the elements and the number of elements required by an array, use a declaration of the form −
The compiler reserves the appropriate amount of memory. (Recall that a declaration, which reserves memory is more properly known as a definition). The arraySize must be an integer constant greater than zero. For example, to tell the compiler to reserve 11 elements for integer array C, use the declaration −
Arrays can be declared to contain values of any non-reference data type. For example, an array of type string can be used to store character strings.
Examples Using Arrays
This section gives many examples that demonstrate how to declare, initialize and manipulate arrays.
Example 1: Declaring an Array and using a Loop to Initialize the Array’s Elements
The program declares a 10-element integer array n. Lines a–b use a For statement to initialize the array elements to zeros. Like other automatic variables, automatic arrays are not implicitly initialized to zero. The first output statement (line c) displays the column headings for the columns printed in the subsequent for statement (lines d–e), which prints the array in tabular format.
Example
Result − It will produce the following result −
Example 2: Initializing an Array in a Declaration with an Initializer List
The elements of an array can also be initialized in the array declaration by following the array name with an equal-to sign and a brace-delimited comma-separated list of initializers. The program uses an initializer list to initialize an integer array with 10 values (line a) and prints the array in tabular format (lines b–c).

Example
Result − It will produce the following result −
Example 3: Summing the Elements of an Array
Often, the elements of an array represent a series of values to be used in a calculation. For example, if the elements of an array represent exam grades, a professor may wish to total the elements of the array and use that sum to calculate the class average for the exam. The program sums the values contained in the 10-element integer array a.
Example
Result − It will produce the following result −
Arrays are important to Arduino and should need a lot more attention. The following important concepts related to array should be clear to a Arduino −
| S.NO. | Concept & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Passing Arrays to Functions To pass an array argument to a function, specify the name of the array without any brackets. |
| 2 | Multi-Dimensional Arrays Arrays with two dimensions (i.e., subscripts) often represent tables of values consisting of information arranged in rows and columns. |
Use Python to communicate between Arduino.
- 2,242 views
- 0 comments
- 0 respects
Components and supplies
Apps and online services
| |
| |
|
About this project
In this tutorial, we are going to learn how we can install python on our computer and how to use it with Arduino, it allows us to send data between a computer though Arduino's serial.
Step 1: Install Python on Your Computer
You can skip this step if you have installed the Python IDLE already in your computer.
1. Go to the python website and download it (here).
2. Once you have done downloading, you can move on to installation by keeping the directory in which the python is getting installed by default.
Step 2: Install PySerial
PySerial is a Python API module which is used to read and write serial data to Arduino or any other Microcontroller. To install on Windows, simply visit PySerial's Download Page and following the steps bellow :
Arduino Serial Read Number Of Bytes
1. Download the PySerial from the link above or Open CMD and type
Arduino Read Number From Serial
2. Install it by keeping the setting as the default. You should be sure that Pyserial worked correctly, To check this You can open IDLE and type in
If you are not getting any error, it means you installed it correct, else you can check your installation.
Step 3: Python Code
First up, we need a simple program to get the Python sending data over the serial port.
Step 4: Arduino Code
To initiate a connection with the Arduino from Python, we first have to figure out which COM Port the Arduino is on. We can simply see in which port our Arduino is on.
Code
Arduino Code Examples
Author
ansh2919
- 4 projects
- 1 follower
Published on
November 6, 2020 you might like
you might like